Leverage trading in cryptocurrency allows traders to amplify their positions using borrowed funds, increasing potential gains—but also risks. Understanding how to calculate crypto leverage is a critical skill for traders who want to manage their positions effectively and minimize potential losses.
This guide breaks down the process of calculating leverage step-by-step, explaining key concepts like margin, position size, and leverage ratios. By mastering these calculations, you’ll gain the expertise to approach leverage trading with confidence, optimize your strategies, and navigate the volatile crypto markets like a seasoned professional.
How to Calculate Crypto Leverage?
Understanding Crypto Leverage
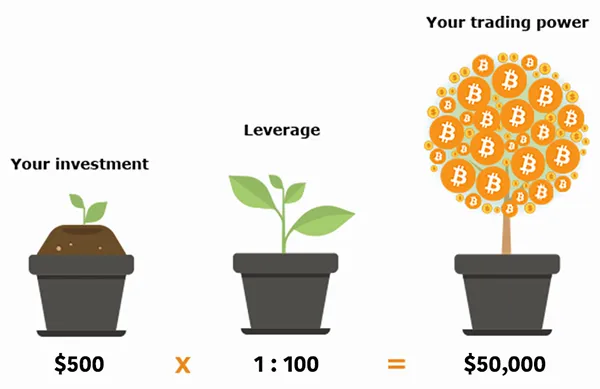
In cryptocurrency trading, leverage refers to the method of gaining a larger exposure to the market than the actual amount of your invested capital. It is essentially borrowed funds provided by a crypto leverage trading exchange to enhance the size of your trades.
When you engage in crypto leverage trading, you are multiplying your trading power. Here’s a simple illustration to help you grasp the concept: If you apply a 10:1 leverage on your position, this means for every $1 of your capital, you are controlling $10 worth of cryptocurrency.
However, leverage is a double-edged sword. Although it can significantly increase potential profits, it also escalates the risk proportionally. You should be aware that losses can exceed your initial investment when using high leverage.
The Basics of Margin Trading
In margin trading, you borrow funds from a broker to trade a larger amount of assets than you currently have in capital. This amplifies both potential gains and losses, making it a powerful but risky tool.
Margin Requirements
Margin requirements dictate the minimum amount of capital you must deposit to open a leveraged position. This is a percentage of the total trade’s value. For example, if you want to open a $10,000 position and the margin requirement is 10%, you must invest $1,000 of your own capital.
Initial Margin and Maintenance Margin
The initial margin is the percentage of a position’s total value that you must deposit to open a trade. It is the starting point for your leveraged trade. The maintenance margin is the minimum balance you must maintain in your account to keep the trade open. If your account balance falls below this threshold, you’ll receive a margin call, requiring you to add more funds or close the position.
Leverage Ratios and Their Calculation
Before diving into the specifics, it’s important to understand that leverage ratios determine the extent to which you employ borrowed capital to enhance your buying power in the market. This mechanism allows traders to magnify their exposure to cryptocurrency markets through leveraged tokens or directly via trading platforms.
Determining Appropriate Leverage Ratio
Your appropriate leverage ratio depends on your risk tolerance, leverage trading strategy, and the market’s conditions. A higher leverage ratio means you’re using more borrowed capital relative to your invested capital. This can significantly increase both potential gains and losses.
In cryptocurrency trading, leveraged tokens represent these ratios inherently, allowing you to hold a position that reflects a multiplied exposure to an underlying asset without managing collateral on a per-trade basis.
Leverage Ratio Formulas
The fundamental formula for leverage is:
Leverage = Position Size / Capital Invested
- Position Size: The total value of the position you’re intending to open, often referred to in Units of the cryptocurrency.
- Capital Invested: The actual amount of your own money that you’re putting into the trade.
To calculate your leverage ratio:
- Choose your cryptocurrency pair, such as BTC-USD.
- Decide on the position size in Units. For example, if you want to open a position equal to 5 BTC.
- Determine your capital investment. This is the amount of money you’re willing to put in, say $1,000.
With this information, your leverage ratio is calculated by dividing the position size by your capital investment. If 5 BTC is worth $100,000 and you invest $1,000, your leverage ratio would be 100 (100,000/1,000). This means for every dollar of your own money, you are exposed to $100 worth of bitcoin, magnifying both potential profits and losses.
Canadian crypto trader? Check these Best Crypto Leverage Trading Exchanges
Executing Leveraged Trades
This section guides you through opening and closing leveraged positions in cryptocurrency trading, detailing the calculation of leverage and its impact on trades.
Opening a Position
When you open a leveraged position, you’re essentially borrowing funds to increase your trading power. Here’s how to approach it:
- Determine Position Size: Decide on the amount you are willing to invest and the degree of leverage you intend to use. Remember that your position size equals your capital multiplied by the leverage ratio.
For example, with a capital of $1,000 and a leverage ratio of 10x, your position size would be:
[\text{Position Size} = $1,000 \times 10 = $10,000] - Choose Long or Short: Decide whether to take a long position (betting that the market will rise) or a short position (betting that the market will fall).
- Set Opening Price: The opening price is your entry point in the market for the position.
- Apply Take-Profit Orders (Optional): Specify the closing price at which your position automatically closes with profit. As a precaution, you may also set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
Closing a Position
To close a leveraged position, you’ll need to exit the market by either hitting a take-profit order or manually closing the trade. Here’s what to consider:
- Closing Price: This is the market price at which you decide to close your position. The difference between the closing price and the opening price will determine your profit or loss.
- Calculate Profit or Loss: The formula for profit or loss is:
[\text{Profit/Loss} = (\text{Closing Price} – \text{Opening Price}) \times \text{Position Size}]
For example, if your opening price was $50,000, the closing price is $55,000, and your position size is $10,000:
[\text{Profit} = ($55,000 – $50,000) \times $10,000 = $50,000,000]
This simplified example doesn’t take into account fees or interest for the borrowed funds which would have to be subtracted from the profit.
Calculating Profit and Loss in Leverage Trading

When engaging in leverage trading with cryptocurrencies, understanding how to calculate your profit and loss (P&L) is crucial.
Leverage allows you to open a larger position with a smaller amount of capital, amplifying both potential gains and losses.
To calculate P&L, you can use the following formula:
Profit or Loss = (Exit Price – Entry Price) x Position Size
- Entry Price: The price at which you enter a trade.
- Exit Price: The price at which you close the trade.
- Position Size: The total size of your leveraged position.
Example:
If you enter a BTC-USD trade at an entry price of $40,000 and exit at $42,000 using a 10x leverage on a $1,000 investment, your calculation would be:
Profit = ($42,000 – $40,000) x (10 x $1,000)
Profit = $2,000 x 10
Profit = $20,000
However, if the market moves against you, the same calculation applies, resulting in losses.
To visualize your P&L at various exit points, consider the following table:
| Exit Price | Profit/Loss |
|---|---|
| $43,000 | $30,000 |
| $41,000 | $10,000 |
| $40,000 | $0 |
| $39,000 | -$10,000 |
| $38,000 | -$20,000 |
It’s important to note that while leverage can increase your profit potential, it also increases the risk of amplified losses.
Always calculate the possible outcomes before entering a trade to understand the risks and returns involved. Also, depending on your region, you might have to pay additional crypto tax on your profit.






